On June 17, 2024, a ransomware attack targeted Indonesia’s national data center, causing a huge data crisis in the country and disrupting more than 280 government agencies. Long queues were formed at immigration gates at Jakarta’s Soekarno-Hatta International Airport as systems were inaccessible because hackers had gained access to their computer system and disrupted normal processing. The attack was carried out using software developed by the Russian ransomware outfit LockBit. Hackers were demanding a $8 million ransom.
On November 23, 2022, the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Delhi was hit by a ransomware attack; hackers allegedly demanded 200 crore INR (about $24.5 million) as ransom.
In February 2023, the ESXiArgs ransomware attack targeted VMware ESXi servers across the world through the RCE vulnerability in VMware ESXi servers. The hackers demanded 2BTC as ransom.
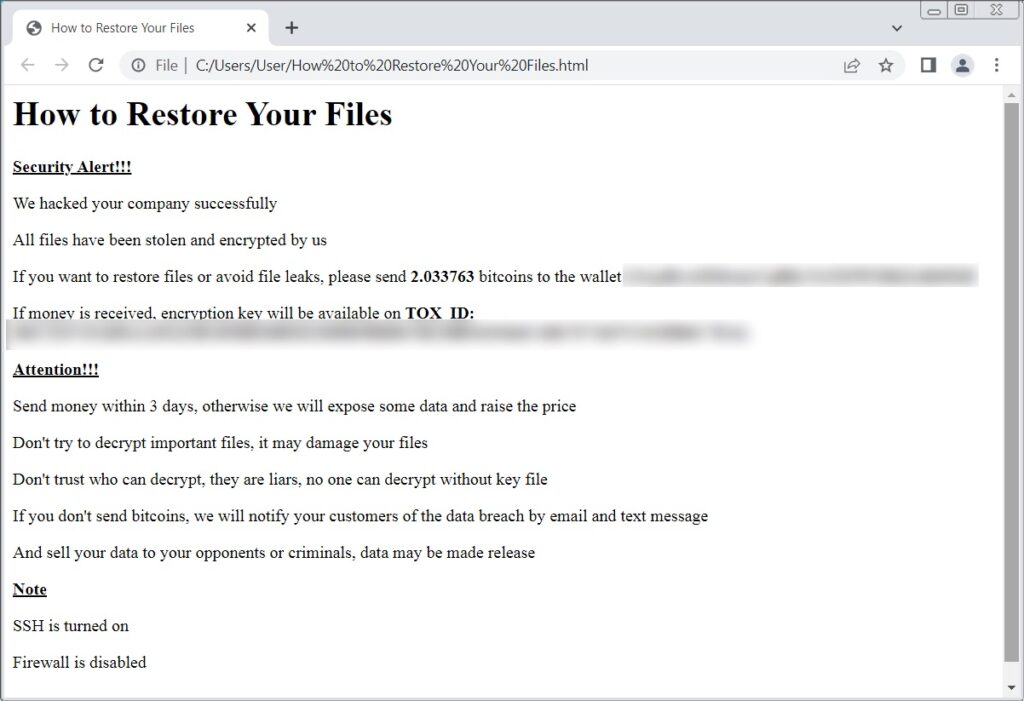
Ransomware attacks are increasing continuously and pose a serious threat to corporate security and identity. A report by cybersecurity firm Sophos shows that hackers are weaponizing stolen data to pressure them for ransom who refuse to pay. They may threaten to publicize the CEO’s contact details or doxing the family members of the target company.
What is Ransomware
Ransomware is malicious software (malware) created and processed to block access to a whole computer system or some file/applications until the ransom is paid.
Basically, hackers infect some files or applications on your systems and encrypt them, which blocks your access to the system or file. By encryption, they take command of your system. Critical applications, files, databases, or confidential data are their main targets while carrying out the attack.
Then, they demand a ransom to provide the decryption key. If everything is okay, users can decrypt their files to gain access. However, there is no promise that your computer will run normally, as all these activities are carried out illegally.
Below are the few common ways hackers gain access to your computer
A CheckPoint study data shows that more than 90% of cyberattacks on businesses start from a malicious phishing email, and 75% of ransomware attacks are email-borne.
Phishing
Phishing is when hackers try to trick people by sending misleading emails, text messages, phone calls, or website links and asking them to share important data like login credentials, card details, and OTP or asking them to download some files secretly containing malware software.
Software Vulnerabilities
Hackers maliciously exploit software vulnerabilities or security flaws in your system or network to gain access to your computer system and install malware like spyware, ransomware, trojan horses, and worms or initiate a DoS attack.
Brute Force Attacks
Brute-force attacks are an effective technique for hackers to gain access to any computer system. In this method, hackers try to crack or guess login credentials passwords by systematically combing letters, numbers, and symbols until they find the correct one.
This is why banks, financial institutions, and other websites recommend using strong passwords and forcing users to change their passwords every three months.
Drive-By Downloads
By this method, hackers install malicious software on your computer without your knowledge; this may happen by accidentally clicking some malicious links or ads or coming in a bundle with third-party applications; this download happens without your consent.
An example: My friend was playing a game on his computer, and a full-screen ad appeared. He saw the ‘X’ button at the top right of the ad and clicked that to close the ad, but he was redirected to another website and then closed that. Within a few days, he noticed the system was not behaving properly; when the internet-connected, full of spam, random ads, popups, slow processing, heating, and auto restart were happening. He accidentally brought a Trojan into his computer system by clicking that ‘X’ button in that ad.
Drive-by downloads are developed mainly to hijack your device, spy on your activity, steal data and login credentials, or damage some files.
Ransomware variant
There are many ransomware variants, such as Ryuk, Maze, REvil (Sodinokibi), Lockbit, DearCry, and Lapsus$—each comes with unique characteristics and impacts.
Ransomware attacks on businesses have risen dramatically over the past few years. Hackers use sophisticated methods to gain computer and network access and demand ransom. Government and private organizations must remain vigilant and implement strong cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risk of being targeted by ransomware attacks.